Cloudpital # 1 is one of the top Remote Patient Monitoring has become a vital part of modern healthcare, offering patients the ability to receive medical care from the comfort of their own homes. By using advanced technology, RPM allows healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health remotely, track vital signs, and respond promptly to any changes. This system not only enhances patient care but also reduces the strain on healthcare facilities, making it a critical tool in today’s medical landscape.
Click to Start Whatsapp Chatbot with Sales
Mobile: +966547315697
Email: sales@cloudpital.com
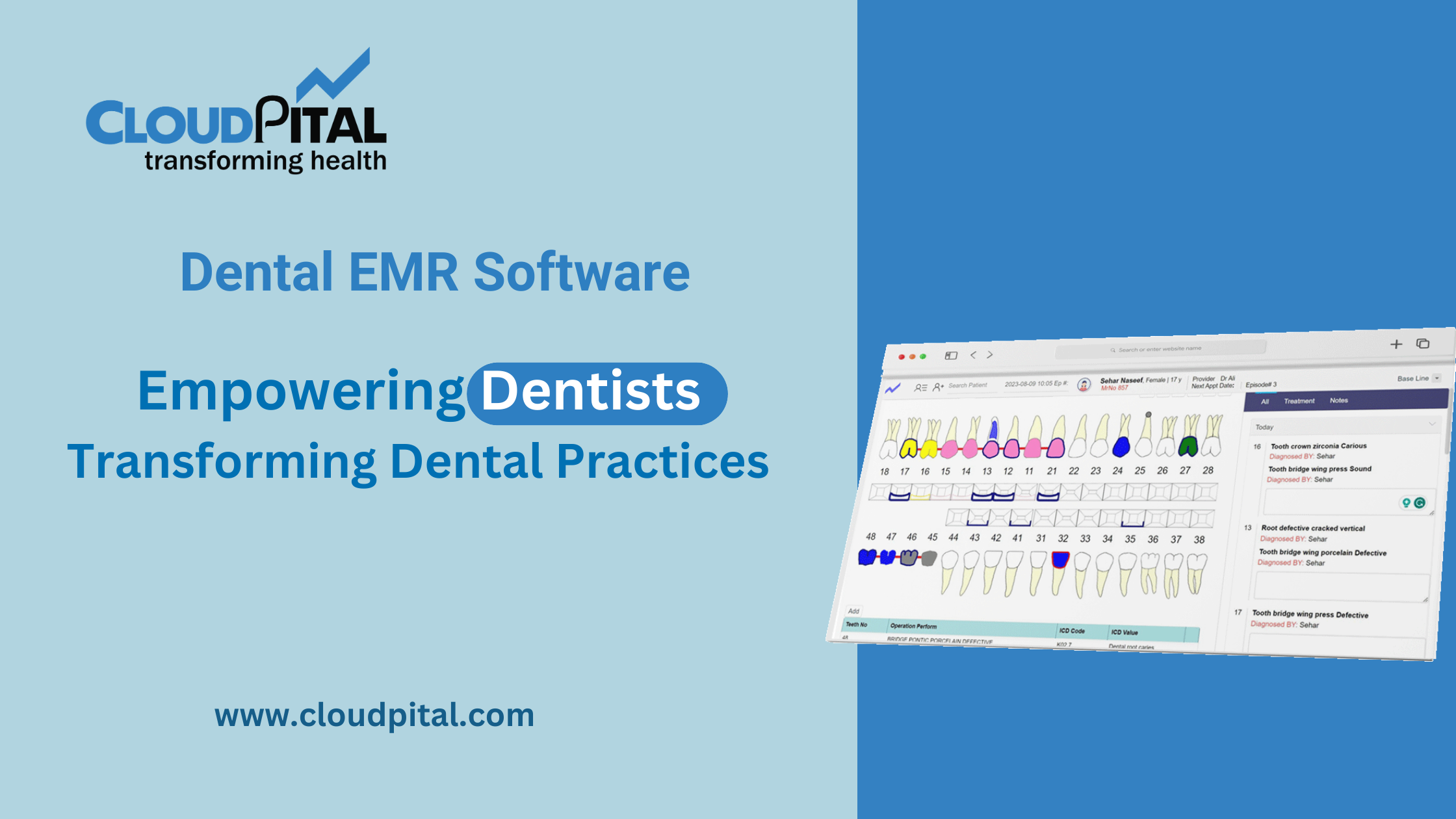
Cloudpital # 1 Remote Patient Monitoring

What is Remote Patient Monitoring?
Remote Patient Monitoring is a healthcare delivery method that uses digital technologies to collect patient data from a distance and transmit it to healthcare providers for assessment, diagnosis, and intervention. It allows doctors to track patients’ conditions in real-time, without the need for frequent in-person visits. This is especially beneficial for managing chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease, where continuous monitoring is essential.
RPM systems collect data such as blood pressure, heart rate, glucose levels, oxygen saturation, and even weight. This data is then sent to healthcare providers through secure communication channels. If any abnormal readings are detected, healthcare professionals can intervene quickly, adjusting medications, recommending lifestyle changes, or advising the patient to seek immediate care.
How Does Remote Patient Monitoring Work?
RPM relies on a combination of devices, software, and communication technologies to function. The process can be broken down into several steps:
- Data Collection: The first step in RPM is gathering patient data. This is done using various medical devices such as wearable sensors, blood pressure monitors, glucometers, and pulse oximeters. These devices are typically easy to use and designed for patients to operate themselves at home.
- Data Transmission: Once the data is collected, it is transmitted to healthcare providers through secure wireless networks. This is often done in real-time or at set intervals, depending on the patient’s condition and the type of monitoring required. The data can be sent via Bluetooth, cellular networks, or Wi-Fi, ensuring seamless communication between the patient and the healthcare provider.
- Data Analysis: Healthcare providers receive the transmitted data through specialized software or dashboards. These platforms analyze the data, identifying trends, deviations from normal ranges, and other critical health indicators. Many RPM systems include algorithms that can alert doctors to concerning patterns, allowing for quick intervention.
- Patient and Provider Communication: If the healthcare provider identifies any issues, they can communicate with the patient directly. This may involve a phone call, video consultation, or even a visit to the healthcare facility if necessary. RPM often incorporates telemedicine features, allowing for real-time discussions between doctors and patients.
- Intervention and Care Adjustment: Based on the data and communication with the patient, healthcare providers can adjust treatments, recommend lifestyle changes, or escalate care. For instance, if a patient with hypertension shows consistently high blood pressure readings, the doctor might increase their medication or advise them to avoid certain foods.
Key Components of Remote Patient Monitoring
RPM systems consist of several key components that work together to deliver remote healthcare effectively:
- Medical Devices: These are the tools patients use to measure their health indicators, such as blood pressure monitors, glucometers, or wearable fitness trackers. The accuracy and ease of use of these devices are critical for the success of RPM.
- Communication Technology: Remote Patient Monitoring systems rely on communication technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks to transmit data. This ensures that patients and healthcare providers remain connected, even when they are miles apart.
- Software and Data Platforms: The software that healthcare providers use to receive, analyze, and store patient data is essential. It often includes advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms that help identify critical patterns in the data.
- Patient Engagement Tools: These tools, such as mobile apps or web portals, allow patients to view their data, communicate with their healthcare providers, and receive reminders or notifications about their health status.

Technologies Involved in Remote Patient Monitoring
Several technologies play a crucial role in making RPM possible:
- Wearable Devices: Wearable technologies, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, allow for continuous monitoring of vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and activity levels. These devices often come with sensors that detect irregularities and alert healthcare providers.
- Mobile Health Apps: Many Hospital Software in Saudi Arabia systems are integrated with mobile health apps, allowing patients to track their health and communicate with their providers. These apps often include reminders, medication tracking, and educational resources for patients to better manage their conditions.
- Cloud Computing and Big Data: The large amount of data generated by RPM systems requires powerful storage and analysis tools. Cloud computing provides scalable storage solutions, while big data analytics allows for the identification of trends and patterns in patient health data.
- Telemedicine Integration: Many RPM systems are integrated with telemedicine platforms, enabling virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers. This combination of RPM and telemedicine ensures continuous care without the need for in-person visits.
Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring
RPM offers numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers:
- Improved Access to Care: RPM enables patients in remote or underserved areas to receive quality healthcare. This is particularly important in countries where access to healthcare facilities may be limited.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: By allowing patients to monitor their own health, RPM encourages active participation in their care. This leads to better adherence to treatment plans and more informed decision-making by patients.
- Early Detection of Health Issues: Continuous monitoring allows healthcare providers to detect potential health problems before they become serious. Early intervention can prevent complications, reduce hospitalizations, and improve outcomes.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: RPM can reduce the need for in-person visits, hospital admissions, and emergency room visits, leading to significant cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems. By preventing complications and managing chronic diseases more effectively, RPM helps lower overall healthcare expenditures.
- Convenience for Patients: Patients can receive care from the comfort of their homes, eliminating the need for frequent trips to healthcare facilities. This is particularly beneficial for elderly or mobility-impaired patients.
- Better Chronic Disease Management: RPM is especially effective in managing chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease, where continuous monitoring is essential for maintaining optimal health.
Challenges and Limitations of Remote Patient Monitoring
Despite its many advantages, RPM also faces certain challenges:
- Data Privacy and Security: The transmission of sensitive health data over the internet raises concerns about privacy and security. Ensuring that patient data is protected from unauthorized access is a critical challenge for RPM providers.
- Technology Adoption: Not all patients may be comfortable using the technology required for RPM, especially older individuals who may not be familiar with smartphones or wearable devices. Training and support are often necessary to help patients use these systems effectively.
- Device Accuracy and Reliability: The accuracy of the medical devices used in RPM is crucial for providing effective care. Inaccurate readings can lead to incorrect diagnoses or inappropriate treatment adjustments.
- Limited Internet Access: In some areas, particularly rural regions, access to reliable internet or cellular networks may be limited, hindering the effectiveness of RPM.
- Regulatory and Reimbursement Challenges: Regulatory frameworks for RPM are still evolving, and reimbursement policies vary by region and healthcare provider. This can limit the widespread adoption of RPM in certain areas.
The Future of Remote Patient Monitoring
The future of RPM looks promising, with advancements in technology expected to drive its growth. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are likely to play a significant role in improving data analysis and predictive capabilities, allowing for even more personalized and proactive care. As telemedicine continues to evolve, its integration with RPM will create a seamless healthcare delivery system that can cater to the needs of patients worldwide.
Furthermore, with the increasing focus on value-based care, Dental Software in Saudi Arabia will become an integral part of healthcare systems, helping to reduce costs while improving patient outcomes. As healthcare providers and policymakers recognize the benefits of RPM, we can expect to see greater investment in infrastructure and technology to support its adoption.
Conclusion
Remote Patient Monitoring has transformed the way healthcare is delivered, offering a convenient, cost-effective, and efficient way to manage patients’ health from a distance. By leveraging advanced technologies, RPM allows healthcare providers to monitor patients continuously, detect potential issues early, and intervene promptly. Although challenges such as data security and technology adoption remain, the future of RPM is bright, with ongoing innovations poised to make remote healthcare even more accessible and effective.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote Patient Monitoring
How does Remote Patient Monitoring work? similar software solutions prices were updated on 2025-06-15T18:09:19+00:00 in Saudi Arabia in Mecca, Medina, Riyadh, Khamis Mushait, Yanbu, Jeddah, Dammam, Unaizah, Uqair, Ha’il, Ta if, Al Bahah, Dhahran, King Abdullah Economic City, Najran, Diriyah, Qatif, Khafji, Jubail, Abqaiq, List of Cities and Towns in Saudi Arabia, Ras Tanura, Turubah, Jazan Economic City, Knowledge Economic City, Medina, Khobar, Abha, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, similar software solutions prices were updated on 2025-06-15T18:09:19+00:00 We also provide in Saudi Arabia services solutions company in Hafar Al-Batin, Udhailiyah, Al-Awamiyah, Hofuf, Hautat Sudair, Buraidah, Tayma, Duba, ‘uyayna, Saihat, Al-Kharj, Al-ula, Jizan, Rumailah, Ar Rass, Arar, Shaybah, Al Majma’ah, Rabigh, Dhurma, Haradh, List of Saudi Cities by Gdp Per Capita, Badr, Sudair Industrial City, Baljurashi, Shaqraa, Al-Khutt, Habala, Ad Dawadimi, Dawadmi, Layla, similar software solutions prices were updated on 2025-06-15T18:09:19+00:00 Price is SAR 100 and this was updated on updated on 2025-06-15T18:09:19+00:00 similar How does Remote Patient Monitoring work? software solutions prices were updated on 2025-06-15T18:09:19+00:00 in Saudi Arabia in Haql, Afif, Al-Abwa, Farasan, Al-Jaroudiya, Thadig, Al-Thuqbah, Al Wajh, Almardmah, Al-Zilfi, Muzahmiyya, Prince Abdul Aziz Bin Mousaed Economic City, Tharmada’a, Skaka, Um Al-Sahek, Sharurah, Tanomah, Bisha, Dahaban, Al Qunfudhah, Qurayyat, Saudi Arabia, Ha’ir, as Sulayyil, Al Lith, Turaif, Al-Gway’iyyah, Samtah, Wadi Ad-Dawasir, Az Zaimah, Safwa City, Jalajil, Harmah, Mastoorah, Hotat Bani Tamim, Jabal Umm Al Ru’us, Rafha, Qaisumah, Al-Ghat, Hajrah, Al-Hareeq. Excerpt: Jeddah (also spelled Jiddah, Jidda, or Jedda; Arabic: Jidda) is a Saudi Arabian city located on the coast of the Red Sea and is the major urban center of western Saudi Arabia similar software solutions prices were updated on 2025-06-15T18:09:19+00:00 Price is SAR 100 and this
5-9-2024