Bilytica # 1 is one of the top Power BI era where data breaches and cyber threats are a growing concern, businesses must prioritize the security of their data, particularly when it involves sensitive information. Power BI, a leading business intelligence tool from Microsoft, is widely used for data analysis, reporting, and visualization. However, as organizations increasingly rely on Power BI to handle sensitive data, questions about its security mechanisms and capabilities have become more pertinent. This article will explore the security features of Power BI, evaluate its ability to handle sensitive data securely, and discuss best practices for ensuring data protection within the platform.
Click to Start Whatsapp Chat with Sales
Call #:+923333331225
Email: sales@bilytica.com
Bilytica #1 Power BI
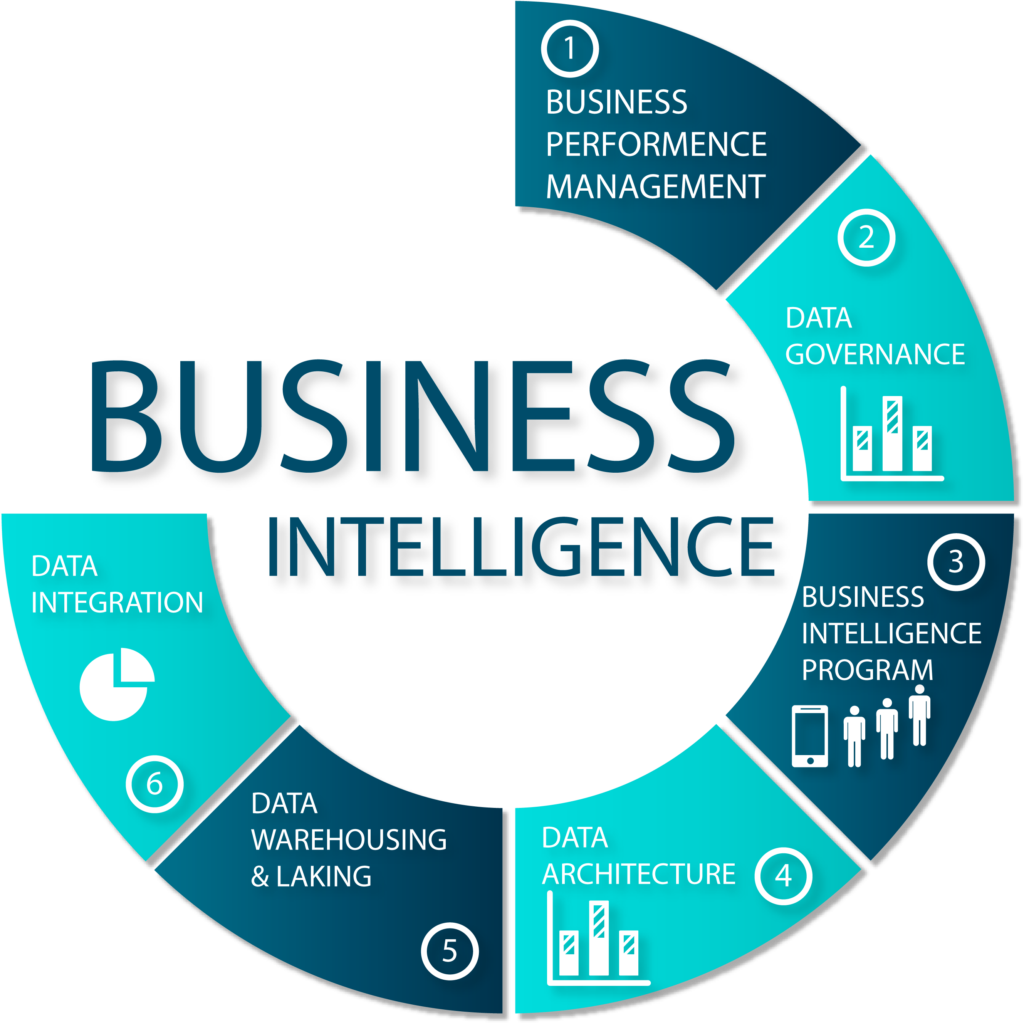
Understanding Power BI’s Security Architecture
Power BI is built on Microsoft’s trusted cloud platform, which incorporates multiple layers of security to protect data throughout its lifecycle. The platform’s security architecture is designed to address concerns related to data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Here’s a breakdown of how Power BI’s security framework works:
Data Encryption
Encryption is one of the most critical security measures for protecting sensitive data in Power BI. The platform employs robust encryption protocols to safeguard data both at rest (stored data) and in transit (data being transmitted across networks).
- Encryption at Rest: Power BI uses AES-256 encryption to protect data at rest. This standard is one of the most secure encryption methods available, ensuring that stored data is unreadable without the correct decryption keys. This applies to data stored in databases, reports, dashboards, and other Power BI assets.
- Encryption in Transit: Data in transit is protected using TLS (Transport Layer Security) encryption, ensuring that any data exchanged between users’ devices and Power BI services remains secure from interception or unauthorized access. This is particularly important when users are accessing Power BI reports and dashboards over the internet.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a fundamental security feature in Power BI that helps organizations manage who has access to what data. RBAC allows administrators to define roles and assign specific permissions to users based on their job responsibilities.
- Workspaces and Permissions: In Power BI, workspaces are used to organize and manage reports, dashboards, and datasets. Each workspace can have its own set of permissions, allowing administrators to control who can view, edit, or share content within that workspace. For instance, a finance workspace may be restricted to only finance team members, while an HR workspace may have different access levels for HR personnel.
- Row-Level Security (RLS): Power BI also supports Row-Level Security, a powerful feature that allows administrators to restrict data access at the row level based on users’ identities. For example, an employee in the sales department may only see sales data relevant to their region, while a manager could have access to data across all regions. RLS ensures that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized individuals, reducing the risk of data exposure.
Compliance with Data Protection Regulations
Compliance with data protection regulations is a key consideration for any organization handling sensitive data. Power BI is designed to help organizations meet various regulatory requirements, including GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and other industry-specific standards.
- Data Residency and Sovereignty: Power BI allows organizations to choose the geographic location of their data centers, ensuring compliance with data residency and sovereignty requirements. This is particularly important for organizations operating in regions with strict data protection laws, such as the European Union or Saudi Arabia. By storing data within the appropriate jurisdiction, organizations can avoid legal complications and ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Audit Logs and Monitoring: Power BI includes comprehensive auditing and monitoring tools that allow organizations to track user activities, access attempts, and data usage within the platform. These logs are essential for demonstrating compliance with data protection regulations and for identifying any potential security incidents. Administrators can set up alerts to notify them of suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access or data sharing, helping to mitigate risks.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a critical component of Power BI’s security strategy. DLP policies help organizations prevent the accidental or intentional sharing of sensitive data outside the organization.
- Content Classification: Power BI supports content classification, allowing organizations to label reports, dashboards, and datasets based on their sensitivity level. For example, content can be labeled as “Confidential,” “Internal,” or “Public.” These labels help users understand the sensitivity of the data they are handling and take appropriate precautions when sharing it.
- Data Sharing Controls: Power BI’s data sharing controls allow administrators to restrict sharing of sensitive content. For instance, administrators can disable sharing of reports or dashboards that contain sensitive data with external users or restrict export options to prevent data from being saved locally. These controls help minimize the risk of data leakage and ensure that sensitive information remains within the organization.

Advanced Threat Protection
Power BI is integrated with Microsoft’s Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) suite, providing additional security layers to protect against cyber threats. ATP uses machine learning and behavioral analytics to detect and respond to potential security threats in real time.
- Anomaly Detection: ATP can identify unusual patterns of behavior, such as an employee accessing a large volume of data outside of normal working hours or from an unfamiliar location. These anomalies may indicate a security breach or unauthorized access, prompting further investigation.
- Automated Responses: In the event of a detected threat, ATP can automatically take action to mitigate the risk, such as blocking access to sensitive data or isolating a compromised user account. This proactive approach helps protect sensitive data from being compromised by cybercriminals.
Challenges and Considerations
While Power BI offers a robust security framework, organizations must also address certain challenges and considerations to ensure the security of sensitive data:
User Awareness and Training
Even with strong security measures in place, human error remains a significant risk factor. Employees who are unaware of data security best practices may inadvertently expose sensitive information. For example, an employee might share a report containing confidential data with unauthorized users or fail to recognize a phishing attempt.
To mitigate this risk, organizations should invest in regular security training for all Power BI users. Training should cover topics such as recognizing phishing attacks, understanding the importance of strong passwords, and adhering to data classification policies. By fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can reduce the likelihood of data breaches caused by human error.
Third-Party Integrations
Power BI is often integrated with other business applications, such as CRM systems, ERP platforms, and data warehouses. While these integrations enhance the functionality of Power BI, they also introduce additional security risks. Data may be exposed if third-party systems do not have the same level of security as Power BI, or if integration points are not adequately secured.
Organizations should conduct thorough security assessments of all third-party integrations and ensure that data is encrypted and protected throughout the integration process. Regular security audits can help identify and address potential vulnerabilities in the integration points.
Managing Data Access Across Devices
As organizations increasingly adopt remote work and bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, managing data access across different devices becomes more challenging. Employees may access Power BI from personal devices, which may not have the same security protections as corporate devices.
To address this challenge, organizations should implement mobile device management (MDM) solutions and enforce security policies for devices accessing Power BI. This includes requiring device encryption, enabling remote wipe capabilities, and restricting access from devices that do not meet security standards.
Balancing Security with Usability
While strong security measures are essential, they should not hinder the usability and efficiency of Power BI. Overly restrictive security policies may frustrate users and lead to workarounds that compromise security. For example, if sharing controls are too restrictive, users might resort to emailing sensitive data instead.
Organizations should strive to balance security with usability by implementing security measures that align with users’ needs and workflows. Engaging users in the development of security policies and providing clear guidance on how to handle sensitive data can help achieve this balance.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Security in Power BI
To maximize the security of sensitive data in Power BI, organizations should follow these best practices:
Implement Strong Access Controls
Ensure that access to Power BI is restricted to authorized users only. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enforce strong password policies. Regularly review user roles and permissions to ensure that they align with job responsibilities.
Regularly Update and Patch Software
Keep Power BI and all associated systems up to date with the latest security patches and updates. This helps protect against known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
Encrypt Data Both at Rest and in Transit
Use encryption to protect sensitive data at all stages of its lifecycle. Ensure that data stored in Business Intelligence Analyst in Saudi Arabia is encrypted using strong encryption protocols, and that data transmitted over networks is secured with TLS encryption.
Monitor and Audit User Activity
Implement monitoring tools to track user activity within Power BI. Regularly review audit logs to detect any unusual behavior or unauthorized access attempts. Set up alerts for potential security incidents and respond promptly to any threats.
Educate Users on Security Best Practices
Provide regular training for all Power BI users on data security best practices. Emphasize the importance of following security policies and procedures, and encourage users to report any suspicious activities.
Conclusion
Power BI is a powerful tool for data analysis and visualization, offering a comprehensive security framework designed to protect sensitive data. With features like encryption, role-based access control, compliance with data protection regulations, and advanced threat protection, Power BI provides robust security measures to safeguard employee and business data.
However, the security of sensitive data in Power BI also depends on how organizations implement and manage these features. By following best practices, conducting regular security assessments, and fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can ensure that their data remains secure while leveraging the full capabilities of Power BI. In an increasingly data-driven world, prioritizing security is essential for organizations that rely on Power BI to make informed decisions and drive business success.
Click to Start Whatsapp Chat with Sales
Call #:+923333331225
Email: sales@bilytica.com
Bilytica #1 Power BI
Power BI
Power BI
Power BI
19-8-2024